Basic IOS Commands
Basic IOS Commands
A Cisco router without a startup-config file will enter in the setup mode, which you can exit to access the Command Line Interface (CLI). The setup mode offers the Basic Management and Extended Setup. You can enter the setup mode again with the command setup at the CLI.
Cursor Commands:
General commands entered in the “#” mode:
clock set hh:mm:ss d month yyyy: sets the current time and date.
show history/terminal: shows last 10 commands (history) or terminal config and history buffer size (terminal).
terminal history size size: sets the history buffer size where size is between 0-256.
terminal no editing: disable or enable the terminal editing keys in the table above.
show version: displays basic IOS and router information, as well as names of config files and boot images, and config register.
show flash: displays the content of the Flash memory, and if only one IOS is in Flash memory, will output the same as show version.
show startup-config/running-config: displays current and NVRAM based configuration files.
copy running-config startup-config: used and required to save the current configuration. Reverse to restore.
erase startup-config: resets the router’s NVRAM. The router will boot in setup mode next time.
ping/trace/telnet: tools provided to verify connectivity. U=Unreachable, ?=Unknown packet received, .=Time down, P=Unreachable port received.
clear counters interface: clears the “show interface” counters on this interface.
show controllers type number: information about the physical interface itself. A space is required between type and number.
reload: reboots the router and reloads the startup-config file.
boot system rom/flash img: indicate what image the router will use during the next boot.
boot system tftp img address: tells the router to use the configuration file img from a tftp server at address.
config terminal/memory/network: used modify the configuration from the running-config, the startup-config or a from a TFTP server.
Commands entered in the Global Configuration “(config)#” mode:
hostname name: used to define a hostname that is locally significant only.
enable [secret] password password: sets enable or secret mode password. secret will override the non-secure password if set and is encrypted.
[no] service password-encryption: encrypts or not (no) the enable and line passwords.
banner login/motd char: sets the login or message of the day banners, where char is the delimiting character.
interface type [slot/]number[.subinterface]. You can skip the space between the interface type and its number. Certain switches equipped with VIP cards use the syntax interface type slot/pan/number[.subinterface] where pan is the Port Adapter Number.
line (vty number number)/(aux/ console number): used to enter the configuration of the console, aux line or VTY lines (telnet).
Commands entered in the “(config-if)#” mode:
description name: used to define a description for the interface. Name must have underscores rather than spaces. show run and show int 0/n will both show the descriptions set on the interfaces.
no shutdown: used and required to bring up an interface. The interface will show as administratively down.
ip address ipaddress subnetmask: used to set the IP address and subnet mask of an interface.
clock rate bps: sets the clock rate on serial ports.
bandwidth kbps: sets the bandwidth of a serial port for routing and STP protocols to establish the best path.
Commands entered in the “(config-line)#” mode:
logging synchronous: stops console msgs from overwriting command line inputs.
exec-timeout min sec: sets the time-out to min sec for the console.
[no] login: used to set the password when followed by password password. A password is required on the VTY lines before Telnet can be used by default unless no login is used.
Router Memory:
ROM: Read-Only Memory which stores the bootstrap startup program, the power-on self-test (POST) procedures and a baseline IOS. The ROM also contains the ROM monitor, used for manufacturing testing and troubleshooting, and the Mini-IOS, or RXBOOT, which can be used to bring up an interface and load a Cisco IOS into flash memory.
Flash Memory: EEPROM (Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) which stores the IOS (Internetwork Operating System).
NVRAM: Non-Volatile Random Access Memory stores the startup config. A switch has a separate VTP NVRAM which can be deleted with the delete vtp command.
RAM or DRAM: Random Access Memory - holds dynamic info such as the current configuration file, the current IOS, caching and buffering.
The Hackers Conference 2013
The Hackers Conference 2013
The Hackers Conference is an unique event, where the best of minds in the hacking world, leaders in the information security industry and the cyber community along with policymakers and government representatives on cyber security meet face-to -face to join their efforts to co-operate in addressing the most topical issues of the Internet Security space.
This is the second edition of the Conference. Following the huge success of the conference last year the current edition of the conference brings back to you all the knowledge, all the fun in a better, grander way! The Conference will be held in New Delhi, on the 25 of August 2013, and will get together industry leaders, Government representatives, Academia and underground Black-hat hackers to share knowledge and leading-edge ideas about information security and everything related to it.
More details :- visit www.thehackersconference.com
General Commands
General Commands
Here is a list of the general commands. These are the basic level commands and most commonly used
no shutdown - (enables the interface)
reload - restarts the router
sh ver - Cisco IOS version, uptime of router, how the router started, where system was loaded from, the interfaces the POST found, and the configuration register
sh clock - shows date and time on router
sh history - shows the history of your commands
sh debug - shows all debugging that is currently enabled
no debug all - turns off all debugging
sh users - shows users connected to router
sh protocols - shows which protocols are configured
banner motd # Your customized message here # - Set/change banner
hostname <give router name> - use to configure the hostname of the router
clear counters - clear interface counters
Privileged Mode commands of a router
Learn how to work in the privileged mode of a router.
enable - get to privileged mode
disable - get to user mode
enable password <give password here> - sets privileged mode password
enable secret <give password here> - sets encrypted privileged mode password
Setting Passwords on router
Here you will be able to learn how to set the password on a router.
enable secret <give password here> - set encrypted password for privileged access
enable password <give password here> - set password for privileged access (used when there is no enable secret and when using older software)
Setting the password for console access:
(config)#line console 0
(config-line)#login
(config-line)#password <put password here>
Set password for virtual terminal (telnet) access (password must be set to access router through telnet):
(config)#line vty 0 4
(config-line)#login
(config-line)#password <put password here>
Set password for auxiliary (modem) access:
(config)#line aux 0
(config-line)#login
(config-line)#password <put password here>
Router Processes & Statistics
By these command you can see the statistics and different processes of the router.
sh processes - shows active processes running on router
sh process cpu - shows cpu statistics
sh mem - shows memory statistics
sh flash - describes the flash memory and displays the size of files and the amount of free flash memory
sh buffers - displays statistics for router buffer pools; shows the size of the Small, Middle, Big, Very Big, Large and Huge Buffers
sh stacks - shows reason for last reboot, monitors the stack use of processes and interrupts routines
IP Commands
Here is a list of the IP Commands
Configure IP on an interface:
int serial 0
ip address 157.89.1.3 255.255.0.0
int eth 0
ip address 2008.1.1.4 255.255.255.0
Other IP Commands:
sh ip route - view ip routing table
ip route <remote_network> <mask> <default_gateway> [administrative_distance] - configure a static IP route
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <put gateway of the last resort here> - sets default gateway
ip classless - use with static routing to allow packets destined for unrecognized subnets to use the best possible route
sh arp - view arp cache; shows MAC address of connected routers
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 secondary - configure a 2nd ip address on an interface
sh ip protocol
CDP Commands (Cisco Discovery Protocol uses layer 2 multicast over a SNAP-capable link to send data):
sh cdp neighbor - shows directly connected neighbors
sh cdp int - shows which interfaces are running CDP
sh cdp int eth 0/0 - show CDP info for specific interface
sh cdp entry <cdp neighbor here> - shows CDP neighbor detail
cdp timer 120 - change how often CDP info is sent (default cdp timer is 60)
cp holdtime 240 - how long to wait before removing a CDP neighbor (default CDP holdtime is 180)
sh cdp run - shows if CDP turned on
no cdp run - turns off CDP for entire router (global config)
no cdp enable - turns off CDP on specific interface
IPX Commands
Enable IPX on router:
ipx routing
Configure IPX + IPX-RIP on an int:
int ser 0
ipx network 4A
Other Commands:
sh ipx route - shows IPX routing table
sh ipx int e0 - shows ipx address on int
sh ipx servers - shows SAP table
sh ipx traffic - view traffic statistics
debug ipx routing activity - debugs IPS RIP packets
debug ipx sap - debugs SAP packets
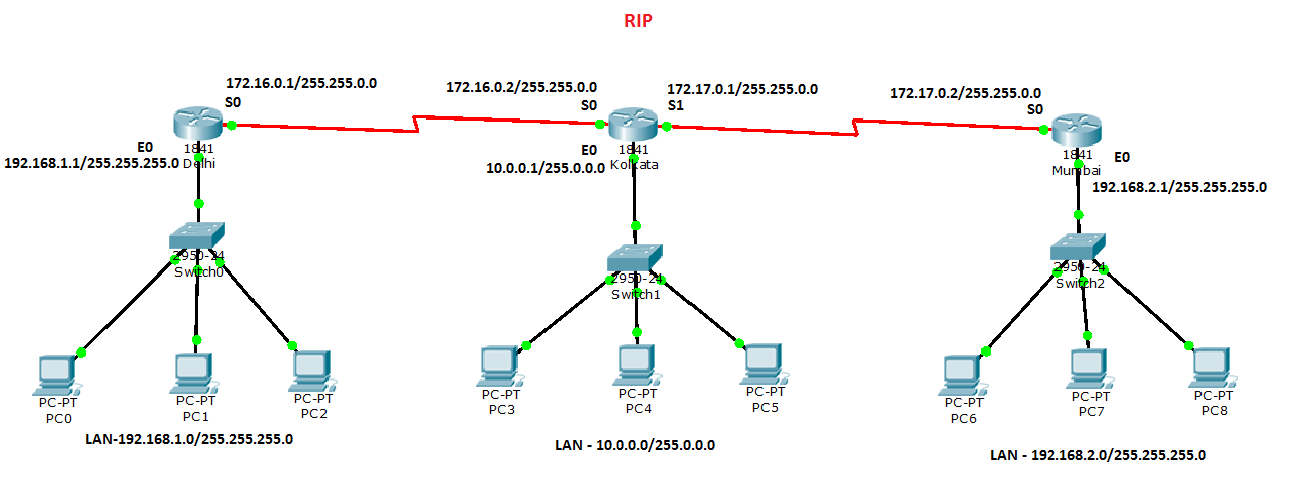
Routing Protocols
RIP, IGPR and OSPF are the routing protocols and here is a list of the commands for the working on the routing protocols.
Configure RIP:
router rip
network 157.89.0.0
network 208.1.1.0
Other RIP Commands:
debug ip rip - view RIP debugging info
Configure IGRP:
router IGRP 200
network 157.89.0.0
network 208.1.1.0
Other IGRP Commands:
debug ip igrp events - view IGRP debugging info
debug ip igrp transactions - view IGRP debugging info
Access Lists
Here is a list of the Access list command of a router.
sh ip int ser 0 - use to view which IP access lists are applies to which int
sh ipx int ser 0 - use to view which IPX access lists are applies to which int
sh appletalk int ser 0 - use to view which AppleTalk access lists are applies to which int
View access lists:
sh access-lists
sh ip access-lists
sh ipx access-lists
sh appletalk access-lists
Apply standard IP access list to int eth 0:
access-list 1 deny 200.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 1 permit any
int eth 0
ip access-group 1 in
Apply Extended IP access list to int eth 0:
access-list 100 deny tcp host 1.1.1.1 host 2.2.2.2 eq 23
access-list 100 deny tcp 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 any eq 80
int eth 0
ip access-group 100 out
Apply Standard IPX access list to int eth 0:
access-list 800 deny 7a 8000
access-list 800 permit -1
int eth 0
ipx access-group 800 out
Apply Standard IPX access list to int eth 0:
access-list 900 deny sap any 3378 -1
access-list 900 permit sap any all -1
int eth 0
ipx access-group 900 out
WAN Configurations Commands
Networking over WAN is the main functionality of a router. The most common use of a router is for the WAN connectivity. Here is a list of the commands for the different methods of the WAN connectivity.
PPP Configuration
Point to point protocol is a method for the WAN connectivity and you will find here some commands of PPP.
encapsulation pppppp authentication <chap or pap here>
ppp chap hostname <put router name here>
ppp pap sent-username <put user name here>
sh int ser 0 - use to view encapsulation on the interface
Frame-Relay Configuration
One of the methods for the WAN connectivity is the Frame Relay. Find here some basic commands for the WAN connectivity through Frame Relay.
encapsulation frame-relay ietf - use IETF when setting up a frame-relay network between a Ciscorouter and a non-Cisco router
frame-relay lmi-type ansi - LMI types are Cisco, ANSI, Q933A; Cisco is the default; LMI type is auto-sensed in IOS v11.2 and up
frame-relay map ip 3.3.3.3 100 broadcast - if inverse ARP won't work, map Other IP to Your DLCI # (local)
keep alive 10 - use to set keep alive
sh int ser 0 - use to show DLCI, LMI, and encapsulation info
sh frame-relay pvc - shows the configured DLCI's; shows PVC traffic stats
sh frame-relay map - shows route mapssh frame-relay lmi - shows LMI info
Miscellaneous Commands
In the last but not least here is a list of the some miscellaneous and useful commands
sh controller t1 - shows status of T1 lines
sh controller serial 1 - use to determine if DCE or DTE device
(config-if)#clock rate 6400 - set clock on DCE (bits per second)
(config-if)#bandwidth 64 - set bandwidth (kilobits)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)